State Athletic Organizations and their heat safety practices
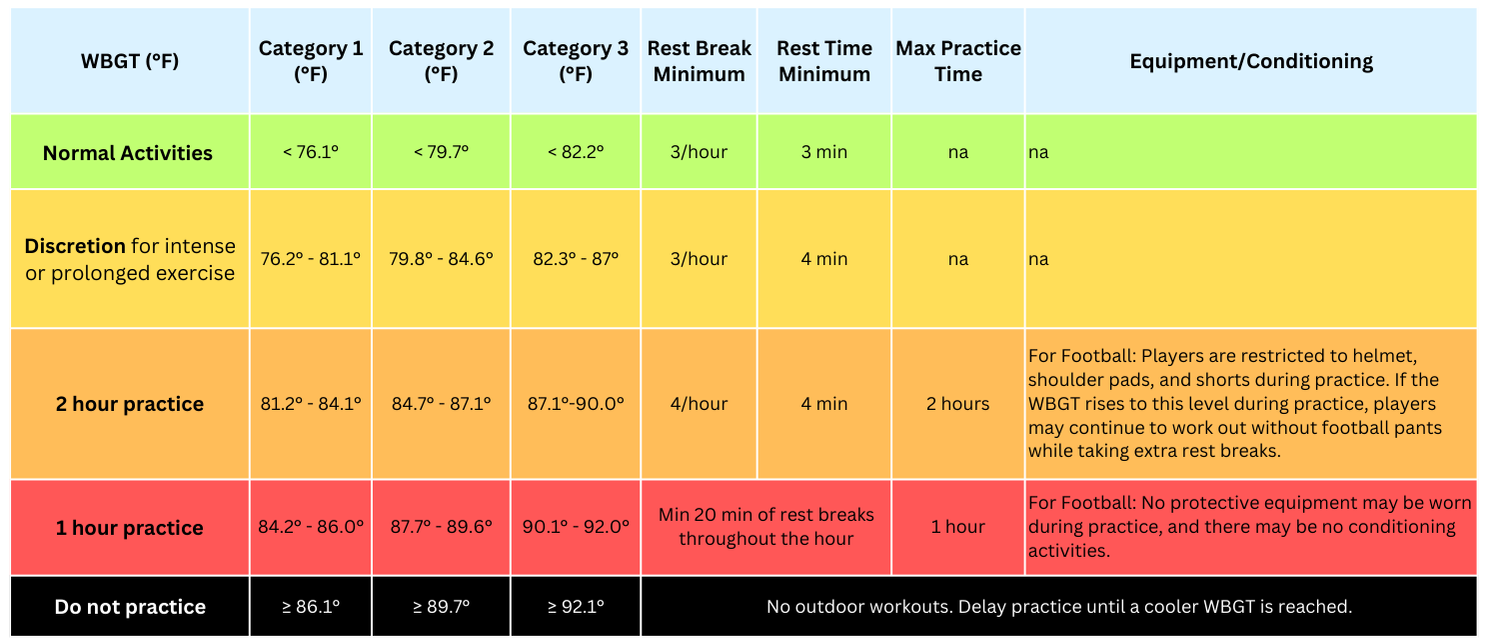
Each state in the US has established their heat illness prevention practices based on the unique criteria of their state and by looking from guidance from the NFHS. Learn more about high school regulations and the NFHS guidelines.
| State | Organization Name | Website URL | Summary |
| Alabama | Alabama High School Athletic Association | www.ahsaa.com | Alabama requires member schools to follow strict heat acclimatization protocols. These include a 14-day acclimatization period where athletes gradually increase activity levels and equipment use. Water breaks must be provided every 20-30 minutes during practices, and activities must be adjusted based on the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT). |
| Alaska | Alaska School Activities Association | www.asaa.org | Alaska's guidelines focus on monitoring temperature and humidity to ensure safe conditions for athletes. While the state's cooler climate results in fewer heat-related risks, schools are encouraged to provide frequent hydration breaks, limit practice duration in warm weather, and educate athletes on recognizing early signs of heat illness. |
| Arizona | Arizona Interscholastic Association | www.aiaonline.org | Arizona emphasizes a robust heat acclimatization policy due to its extreme temperatures. Over a 14-day period, athletes increase exposure to heat and equipment. Practices are limited in duration and intensity during the first five days, with mandatory water breaks every 15 minutes and strict monitoring of WBGT. Outdoor activities are modified or canceled when WBGT readings exceed safety thresholds. |
| Arkansas | Arkansas Activities Association | www.ahsaa.org | Arkansas requires schools to monitor WBGT and follow specific guidelines for modifying or canceling practices based on readings. Hydration is a top priority, and schools must provide shaded areas or cooling zones. Practices in full gear are limited during the acclimatization period, and activities may be suspended when WBGT exceeds critical thresholds. |
| California | California Interscholastic Federation | www.cifstate.org | California mandates a detailed heat illness prevention plan, requiring schools to monitor environmental conditions using WBGT or equivalent measures. Coaches must be trained in heat illness recognition and response. Water breaks are enforced every 20 minutes, and shaded recovery areas are mandatory for overheated athletes. Practices are modified or canceled at high WBGT levels. |
| Colorado | Colorado High School Activities Association | www.chsaanow.com | Colorado recommends a 14-day heat acclimatization protocol with gradual intensity increases. Schools are advised to monitor WBGT and implement activity modifications based on temperature and humidity. Hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes and shaded recovery areas are strongly encouraged. |
| Connecticut | Connecticut Interscholastic Athletic Conference | www.casciac.org | Connecticut uses WBGT to guide practice modifications. Practices are canceled when WBGT exceeds 89.9°F. The guidelines also emphasize gradual acclimatization, hydration every 20 minutes, and a maximum practice time of 3 hours per day during the initial 14-day acclimatization period. Rest breaks are mandatory, and all coaches are trained in recognizing heat-related illnesses. |
| Delaware | Delaware Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.doe.k12.de.us | Delaware mandates a 14-day acclimatization period with gradual progression in activity and equipment usage. Activities are modified or canceled based on WBGT readings. Hydration breaks are required every 20-30 minutes, and shaded or cooling areas must be accessible. Coaches receive training in heat illness prevention and treatment. |
| Florida | Florida High School Athletic Association | www.fhsaa.com | Florida’s guidelines are among the strictest due to the state’s high temperatures and humidity. WBGT readings are mandatory for all outdoor practices, with specific thresholds for modifying or canceling activities. Cooling zones and cold water immersion tanks must be available. Coaches are required to complete annual heat illness prevention training. Athletes must follow a 14-day acclimatization period. |
| Georgia | Georgia High School Association | www.ghsa.net | Georgia employs WBGT-based activity guidelines. Practices are limited to two hours during the acclimatization period, and full gear is not permitted until day six. Practices must be modified or canceled if WBGT exceeds 92°F. Hydration is required every 20-30 minutes, and rest breaks must increase in duration as WBGT levels rise. |
| Hawaii | Hawaii High School Athletic Association | www.sportshigh.com | Hawaii’s heat safety plan includes a 14-day acclimatization period with gradual increases in practice intensity and equipment use. Water breaks are required every 20-30 minutes. WBGT monitoring is encouraged, with recommendations for modifying or canceling activities based on high readings. |
| Idaho | Idaho High School Activities Association | www.idhsaa.org | Idaho recommends monitoring temperature and humidity to ensure safe practice conditions. The state advises gradual acclimatization and hydration breaks every 30 minutes. Coaches must educate athletes on the signs and symptoms of heat illness and emphasize early intervention. |
| Illinois | Illinois High School Association | www.ihsa.org | Illinois mandates the use of WBGT to assess practice conditions. Practices must be modified or canceled based on WBGT thresholds, with mandatory water breaks every 20 minutes. Coaches are required to complete training in heat illness prevention. Rest breaks increase in length as WBGT rises, and practices are prohibited above a WBGT of 92°F. |
| Indiana | Indiana High School Athletic Association | www.ihsaa.org | Indiana implements a 14-day heat acclimatization program, limiting the intensity and duration of practices during the initial days. Athletes are required to have frequent hydration breaks, and WBGT monitoring is recommended for adjusting practices. Coaches must receive training in heat illness prevention. |
| Iowa | Iowa High School Athletic Association | www.iahsaa.org | Iowa follows a gradual 14-day heat acclimatization schedule with restrictions on equipment use and practice duration. Hydration breaks are mandatory every 20-30 minutes. WBGT is encouraged for monitoring conditions, and activities may be canceled or modified during extreme heat. Coaches are required to educate athletes on heat illness symptoms. |
| Kansas | Kansas State High School Activities Association | www.kshsaa.org | Kansas mandates a 14-day acclimatization period during which athletes gradually adapt to heat and equipment use. Practices are restricted to three hours per day during this period. WBGT monitoring is encouraged, and hydration breaks must occur every 30 minutes or more frequently as needed. |
| Kentucky | Kentucky High School Athletic Association | www.khsaa.org | Kentucky requires schools to monitor WBGT and implement modifications based on the heat index. Activities must be postponed or canceled if WBGT exceeds 92°F. Coaches and athletic staff are trained in heat illness prevention. Water breaks are mandatory every 15-20 minutes, and cooling zones must be provided for athletes during high heat. |
| Louisiana | Louisiana High School Athletic Association | www.lhsaa.org | Louisiana implements a mandatory 14-day heat acclimatization period. Practices are restricted in duration, and breaks must be provided every 20-30 minutes. WBGT monitoring is recommended for modifying or canceling practices, and schools must have emergency response plans for heat illness. |
| Maine | Maine Principals' Association | www.mpa.cc | Maine focuses on hydration, gradual acclimatization, and monitoring environmental conditions. Water breaks are mandatory every 30 minutes, and practices are modified or canceled in high heat conditions. Coaches are required to educate athletes on recognizing the signs of heat-related illnesses. |
| Maryland | Maryland Public Secondary Schools Athletic Association | www.mpssaa.org | Maryland enforces a 14-day acclimatization period with limits on practice duration and intensity. Schools are required to monitor WBGT to adjust practices or games during extreme heat. Water breaks every 20-30 minutes are mandatory, and shaded recovery areas must be available. Coaches are trained annually in heat illness recognition and prevention. |
| Massachusetts | Massachusetts Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.miaa.net | Massachusetts requires schools to monitor WBGT or equivalent measures to adjust outdoor activities. A gradual acclimatization plan is mandated, and practices must follow hydration and rest guidelines. Coaches are trained to recognize early signs of heat illness, and water breaks are enforced at least every 30 minutes. |
| Michigan | Michigan High School Athletic Association | www.mhsaa.com | Michigan mandates activity modifications based on WBGT readings. Activities are suspended when WBGT exceeds 89°F. Practices during the first 14 days must focus on acclimatization, with limits on intensity and duration. Coaches must provide water breaks every 20-30 minutes and ensure recovery areas are available. |
| Minnesota | Minnesota State High School League | www.mshsl.org | Minnesota requires a 14-day heat acclimatization period with a focus on gradually increasing intensity and duration. Schools must monitor environmental conditions, adjust practices accordingly, and provide hydration breaks at least every 20 minutes. Coaches must educate athletes on heat illness symptoms and treatment. |
| Mississippi | Mississippi High School Activities Association | www.misshsaa.com | Mississippi emphasizes strict adherence to WBGT-based protocols. Practices are modified or canceled when WBGT exceeds safe levels. Hydration is enforced every 20-30 minutes, and schools must provide cooling areas or cold immersion tubs for emergencies. Coaches are required to complete heat illness prevention training. |
| Missouri | Missouri State High School Activities Association | www.mshsaa.org | Missouri implements a 14-day acclimatization period with progressive intensity increases. WBGT readings guide practice modifications, and activities are suspended above certain thresholds. Frequent hydration breaks are required, and coaches are educated annually on heat illness prevention and management. |
| Montana | Montana High School Association | www.mhsa.org | Montana recommends acclimatization and hydration strategies for student-athletes, with breaks every 20-30 minutes during practices. While the state experiences less extreme heat, schools are encouraged to monitor environmental conditions and educate coaches and athletes on recognizing heat illness. |
| Nebraska | Nebraska School Activities Association | www.nsaahome.org | Nebraska requires a 14-day acclimatization period with gradual increases in activity intensity and duration. Schools are encouraged to monitor WBGT to adjust or cancel practices during extreme heat. Hydration breaks must occur every 20-30 minutes, and shaded recovery areas are recommended. |
| Nevada | Nevada Interscholastic Activities Association | www.niaa.com | Nevada mandates the use of WBGT to guide practice and game modifications. Practices must be adjusted or canceled if thresholds are exceeded. Hydration is emphasized, with water breaks required every 15-30 minutes. Coaches are trained in heat illness prevention and emergency response. |
| New Hampshire | New Hampshire Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.nhiaa.org | New Hampshire enforces a 14-day acclimatization period with limits on practice duration and intensity. WBGT monitoring is recommended, and hydration breaks every 20 minutes are mandatory. Coaches must educate athletes about heat illness signs and ensure recovery areas are accessible. |
| New Jersey | New Jersey State Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.njsiaa.org | New Jersey uses WBGT readings to adjust or cancel practices and games. Activities are restricted if WBGT exceeds 90°F. A 14-day acclimatization period is required, and water breaks are enforced every 15-30 minutes. Coaches are trained in heat illness recognition and emergency action plans. |
| New Mexico | New Mexico Activities Association | www.nmact.org | New Mexico implements WBGT-based activity modifications. Practices are restricted or canceled above certain thresholds. A gradual acclimatization period is required, and hydration breaks must occur every 15-20 minutes. Cooling zones are recommended for recovery during extreme heat. |
| New York | New York State Public High School Athletic Association | www.nysphsaa.org | New York requires WBGT monitoring to adjust activities based on heat levels. Practices are canceled or restricted when WBGT reaches unsafe thresholds. The state mandates hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes and provides guidelines for a 14-day acclimatization period. Coaches are trained to recognize and treat heat illness. |
| North Carolina | North Carolina High School Athletic Association | www.nchsaa.org | North Carolina has strict heat safety guidelines, requiring WBGT monitoring for all outdoor practices. Activities are modified or canceled based on WBGT readings. Schools must provide hydration breaks every 15-20 minutes, shaded recovery areas, and emergency action plans. Coaches are trained annually in heat illness prevention. |
| North Dakota | North Dakota High School Activities Association | www.ndhsaa.com | North Dakota emphasizes hydration and gradual acclimatization during a 14-day period. Schools are encouraged to monitor environmental conditions and modify activities during extreme heat. Water breaks are required every 20-30 minutes, and coaches must educate athletes on heat illness symptoms. |
| Ohio | Ohio High School Athletic Association | www.ohsaa.org | Ohio mandates WBGT monitoring to adjust or cancel practices when conditions exceed safe thresholds. A 14-day acclimatization period is required, limiting full equipment usage and practice duration. Hydration breaks must be provided every 20-30 minutes, and emergency action plans for heat illness are required. |
| Oklahoma | Oklahoma Secondary School Activities Association | www.ossaa.com | Oklahoma emphasizes WBGT monitoring to ensure safe practice conditions. Activities are restricted or canceled when WBGT levels exceed certain thresholds. Hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes are mandatory, and schools must implement a gradual acclimatization plan over 14 days. |
| Oregon | Oregon School Activities Association | www.osaa.org | Oregon requires a 14-day heat acclimatization period, with strict limits on practice duration and intensity during the first days. WBGT monitoring is used to guide activity modifications. Hydration is emphasized, with breaks every 20-30 minutes, and coaches must educate athletes about heat illness prevention. |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.piaa.org | Pennsylvania mandates WBGT monitoring and activity modifications during high heat. A 14-day acclimatization period is required, with restrictions on practice duration and equipment use. Water breaks every 15-30 minutes and shaded recovery areas are emphasized. |
| Rhode Island | Rhode Island Interscholastic League | www.riil.org | Rhode Island enforces WBGT monitoring to adjust or cancel activities. The guidelines include a 14-day acclimatization period with progressive activity intensity and equipment use. Hydration breaks are required every 20-30 minutes, and coaches must be trained in recognizing heat illness. |
| South Carolina | South Carolina High School League | www.schsl.org | South Carolina uses WBGT readings to guide activity modifications and cancellations. A 14-day acclimatization period is mandatory, with restrictions on practice intensity and duration. Water breaks every 20-30 minutes are required, and schools must provide shaded recovery areas and cooling strategies. |
| South Dakota | South Dakota High School Activities Association | www.sdhsaa.com | South Dakota recommends WBGT monitoring for adjusting or canceling practices in extreme heat. A 14-day acclimatization period with progressive intensity is required. Hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes and education on heat illness symptoms are emphasized. |
| Tennessee | Tennessee Secondary School Athletic Association | www.tssaa.org | Tennessee enforces WBGT monitoring to guide practice modifications or cancellations. A 14-day acclimatization period with limited equipment use and reduced practice duration is required. Schools must provide hydration breaks every 20 minutes and cooling zones for recovery during high heat. |
| Texas | University Interscholastic League | www.uiltexas.org | Texas requires WBGT monitoring for all outdoor activities, with adjustments to practice intensity and duration based on thresholds. The 14-day acclimatization period gradually increases activity levels, limiting full equipment use initially. Water breaks are mandated every 20 minutes, and schools must provide cooling zones or shaded areas. |
| Utah | Utah High School Activities Association | www.uhsaa.org | Utah emphasizes the importance of WBGT monitoring to modify or cancel practices. A 14-day acclimatization period is required, limiting practice duration and intensity during the first week. Hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes are mandatory, and coaches must educate athletes about heat illness symptoms. |
| Vermont | Vermont Principals’ Association | www.vpaonline.org | Vermont’s guidelines stress gradual acclimatization over 14 days and hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes. Schools are encouraged to monitor WBGT and adjust practices during extreme heat. Recovery areas and heat illness education for coaches and athletes are prioritized. |
| Virginia | Virginia High School League | www.vhsl.org | Virginia mandates WBGT monitoring and a 14-day acclimatization period. Practices are adjusted or canceled when WBGT exceeds safety thresholds. Water breaks are required every 15-30 minutes, and cooling zones or shaded areas must be provided. Coaches are trained annually in heat illness prevention. |
| Washington | Washington Interscholastic Activities Association | www.wiaa.com | Washington enforces a 14-day acclimatization period with limits on practice intensity and duration. Schools must monitor WBGT to adjust activities and provide hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes. Coaches are required to educate athletes on heat illness prevention. |
| West Virginia | West Virginia Secondary School Activities Commission | www.wvssac.org | West Virginia requires WBGT monitoring for adjusting or canceling outdoor activities. The state mandates a 14-day acclimatization period and emphasizes hydration every 20-30 minutes. Cooling zones and emergency response plans for heat illness are also required. |
| Wisconsin | Wisconsin Interscholastic Athletic Association | www.wiaawi.org | Wisconsin mandates heat acclimatization over 14 days, with progressive intensity increases. WBGT monitoring is encouraged, and water breaks are required every 20-30 minutes. Schools must provide shaded areas or cooling zones and educate coaches and athletes on heat illness symptoms. |
| Wyoming | Wyoming High School Activities Association | www.whsaa.org | Wyoming emphasizes gradual acclimatization, hydration breaks every 20-30 minutes, and monitoring environmental conditions. Practices are modified or canceled based on heat levels. Coaches must educate athletes about recognizing and managing heat-related illnesses. |